- Climate
Prof. John Christy incorrectly claims to show climate models are too sensitive to carbon dioxide
Key takeaway
There are many reasons why a climate model projection may not perfectly match observations of some aspect of Earth's climate over a given time period, including short-term variability, differences between real-world and simulated emissions, and even measurement errors. Prof. Christy asserts that models are too sensitive to CO2 but provides no evidence to support that claim. Other research has concluded that Prof. Christy's assertion is incorrect.
Reviewed content

Verdict:
Claim:
the real atmosphere is less sensitive to CO2 than what has been forecast by climate models
Verdict detail
Inadequate support: Prof. Christy's study does not provide the evidence to support this conclusion, which contradicts many other published studies.
Full Claim
From our observations we calculated that value as 1.1 C (almost 2° Fahrenheit), while climate models estimate that value as 2.3 C (about 4.1° F). Again, this indicates the real atmosphere is less sensitive to CO2 than what has been forecast by climate models.

Scientist, University of Bonn, Germany
He said without providing evidence for this claim. There are many independent lines of evidence on the sensitivity of the global temperature to changes in carbon dioxide concentrations. From basic physics, a large number of different period with climatic changes in the deep past and the cooling observed for volcano eruptions.
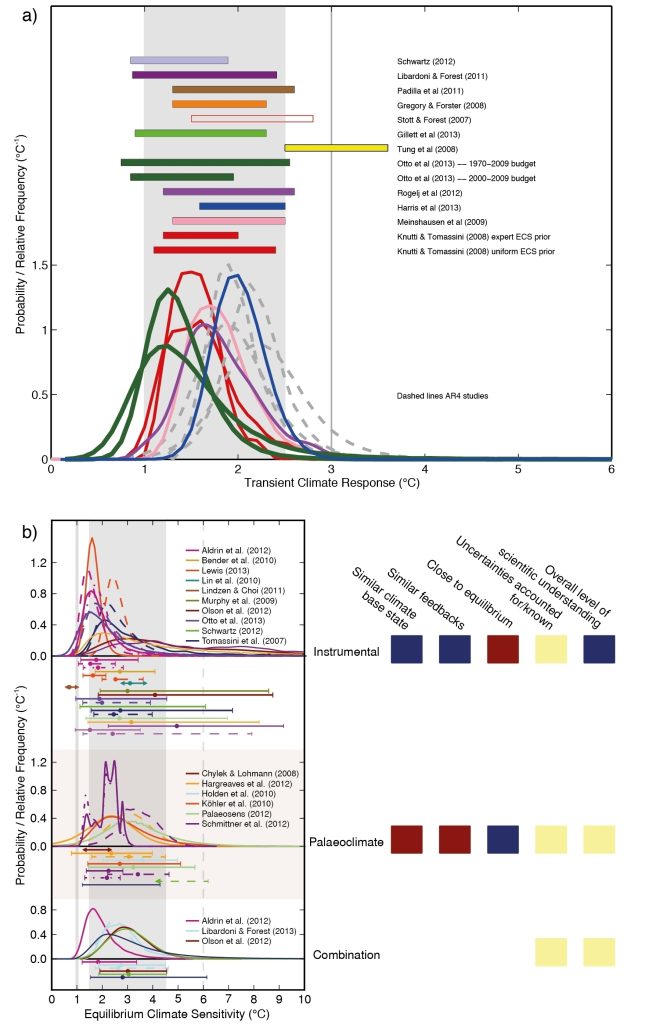
Source: IPCC

Research Scientist, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
While others have documented differences in the rate of warming between models and observations, this study is different in that the authors suggest that these differences are because models are too sensitive to increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Several studies disagree with this assessment in both the surface and atmospheric record.
Other factors contribute to this apparent discrepancy (and some are noted in the original study). These include the potential for observational biases, errors in external forcing prescribed to the models, and real world multidecadal climate variability. So the attribution of model-observational differences predominantly to models is not supported.
- Richardson et al (2016) Reconciled climate response estimates from climate models and the energy budget of Earth, Nature Climate Change
- Santer et al (2017): Causes of differences in model and satellite tropospheric warming rates, Nature Geoscience

Research Associate, Harvard University
This claim is not substantiated by the study. There are several hypotheses to explain why model trends and observations do not agree—internal variability, errors in forcings, model error. Mr. Christy favors the last one, but, as far as I can tell, his study makes no effort to analyse the plausibility of different causes (in fact, it seems they explicitly assume that internal variability and forcing error are not a cause). The other study cited in this piece, Ben Santer’s paper*, goes much further and actually tries to evaluate the plausibility of each hypothesis—and, as the article mentions, comes to different conclusions.
Note also that surface warming in models is in agreement with observations. The question is then why atmospheric warming seems to not be—the models appear to run a little warm there over the last two decades.
- Santer et al (2017): Causes of differences in model and satellite tropospheric warming rates, Nature Geoscience

Professor, ETH Zürich
[This comment is taken from an evaluation of a similar statement.]
Statements that climate models overestimate the warming in response to CO2 are incorrect; they are based on either too short time periods that are dominated by natural variability, by the comparison of models with datasets that do not have global coverage, by comparing to models that were run many years ago with emissions and forcings that differed from what actually happened, by the use of oversimplified energy balance models1, or a combination of these. Recent studies have shown that once the changes in climate feedbacks over time2, datasets with full coverage3, and all forcings are considered, the agreement between predicted and observed warming is excellent, even over the recent hiatus period4.
It is remarkable that even projections made decades ago with climate models that were much simpler (and were running on computers that were likely slower than a mobile phone today) were quite accurate5,6,7.
- 1- Knutti and Rugenstein (2015) Feedbacks, climate sensitivity and the limits of linear models, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A
- 2- Armour (2017) Energy budget constraints on climate sensitivity in light of inconstant climate feedbacks, Nature Climate Change
- 3- Richardson et al (2016) Reconciled climate response estimates from climate models and the energy budget of Earth, Nature Climate Change
- 4- Medhaug et al (2017) Reconciling controversies about the ‘global warming hiatus’, Nature
- 5- Stouffer and Manabe (2017) Assessing temperature pattern projections made in 1989, Nature Climate Change
- 6- Fischer and Knutti (2016) Observed heavy precipitation increase confirms theory and early models, Nature Climate Change
- 7- Allen et al (2013) Test of a decadal climate forecast, Nature Geoscience

Professor, University of New South Wales
[This comment is taken from an evaluation of a similar statement.]
Climate Sensitivity has been assessed by the community based on recent observations and proxy data from past climates. Climate models fall within this range of sensitivity. Some recent publications point to an increase in sensitivity with warmer temperatures*.
- Paleosens Project Members (2013) Making sense of palaeoclimate sensitivity, Nature
- Meraner et al (2013) Robust increase in equilibrium climate sensitivity under global warming, Geophysical Research Letters
- Zeebe (2013) Time-dependent climate sensitivity and the legacy of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences