- Health
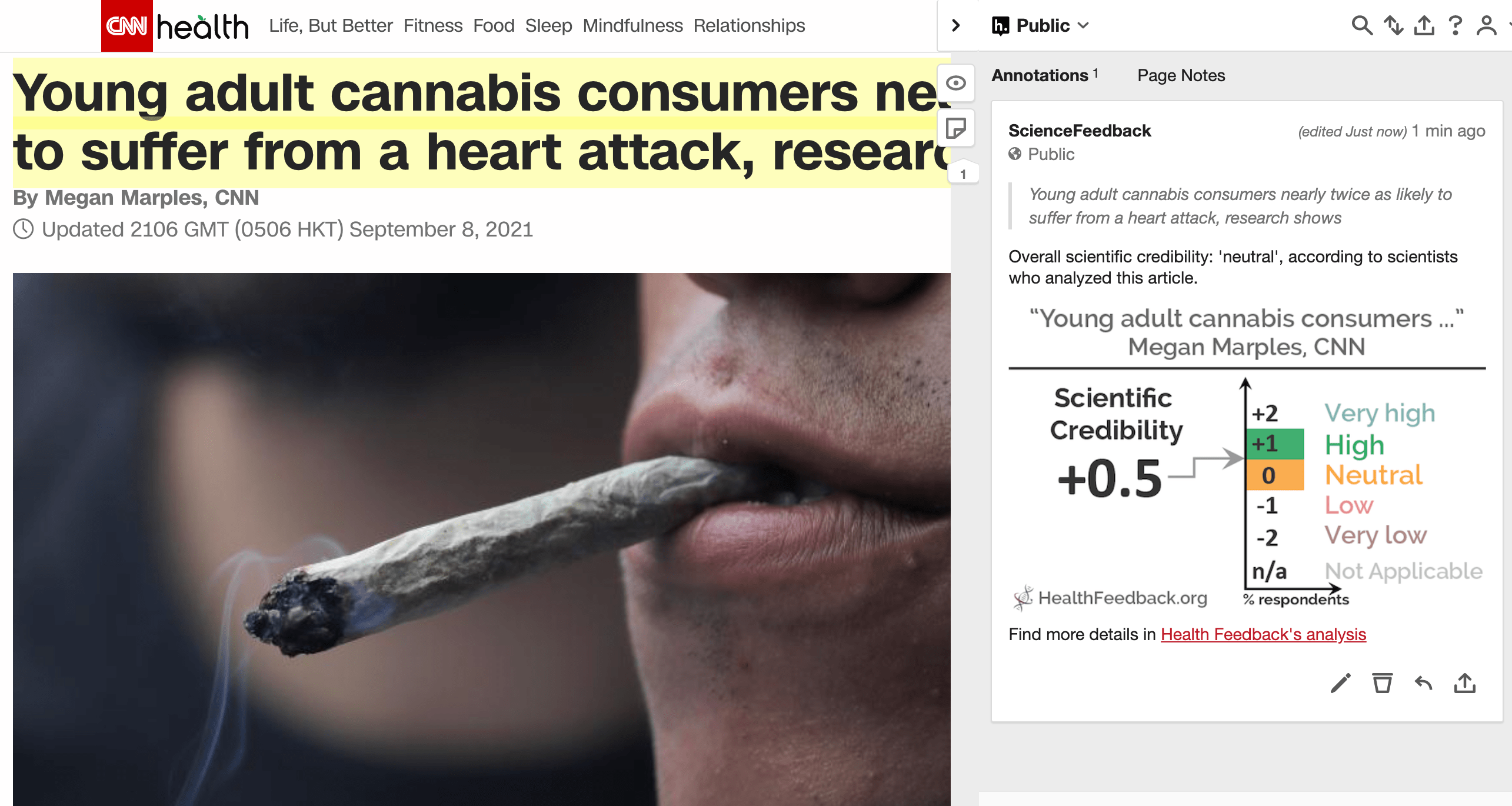
News article accurately reports negative impact of marijuana on teens’ intellectual development
Key takeaway
Although more work is still needed to clearly understand marijuana's effect on adolescents’ intellectual development, the general scientific consensus, based on current evidence, is that marijuana does cause a decline in cognitive function. In light of the significant brain development during adolescence, it may be prudent for teens to avoid using the drug.
Reviewed content

Verdict:
Claim:
Marijuana could be making teens less intelligent
Verdict detail
Correct: The article accurately describes a study showing teenagers who smoke marijuana frequently have a lower IQ as adults, a result supported by available evidence.
Full Claim
Marijuana could be making teens less intelligent. A study found teenagers who use marijuana at least four days a week lost 8 IQ points between the ages of 13 and 38.
Summary
This article by KHOU reports the findings of a research study on the effect of marijuana (also known as cannabis) smoking, performed on a cohort in New Zealand (the Dunedin study). The study’s results showed that individuals who smoked marijuana frequently (at least 4 days a week) beginning in adolescence lost 8 IQ points by adulthood compared to individuals that did not smoke marijuana. However, this reduction in IQ score was not observed in individuals who started smoking only in adulthood.
The study’s findings suggest that marijuana smoking in adolescence may have long-term consequences for individuals, such as in their job prospects and job performance.
Reviewers generally agreed that the claim was supported by the current evidence, although they also highlighted that intelligence is a trait that can be influenced by many factors (such as socioeconomic status, prior drug use). Therefore, such studies need to be well designed and controlled to be meaningful. It is also important to keep in mind that associational studies (such as the one reported by the article) can only suggest, but cannot prove a cause-and-effect relationship.
Scientists’ Feedback

Assistant Professor, School of Medicine, Vanderbilt University
The basis for this news story is an article from the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences, published in 2012 by Meier et al[1]. The research group behind this study has a long-standing interest in potential cognitive consequences of cannabis use. As you can imagine, this can be difficult to study, similar to any studies of potentially toxic compounds. It would not be ethical to perform a randomized controlled trial where we would give children cannabis, or alcohol, or weed killer, and then study them years down the road to see if we damaged their brain. As such, we rely on retrospective data, survey people about what they did, or longitudinal cohort trials, where you study a group of people over a long period of time.In this study, Meier et al. reported the most prominent IQ drop in people who started using cannabis as a teen and continued to use over time. Like with other studies, there are concerns that socioeconomic status or alcohol use contributed to the findings. Socioeconomic status is an issue for many reasons, including access to potentially “better” schools or families which focus more on education. Or pragmatically, if you haven’t eaten and are hungry as a child, you may worry more about where your next meal will come from than about learning in school. Nutrition is also a big part of healthy brain development. Alcohol is clearly an issue because it is long known that it can be neurotoxic. In a response to commentaries expressing concern about this[2], the authors showed that when additional controls for socioeconomic status were done, the IQ decrease was still present.
In an interesting follow-up study, the same group reported that over a shorter time frame, from age 12-18, there was not a decline in IQ, but interestingly, IQs were lower in the teens who used cannabis versus those that did not both prior to and after using cannabis[3].
This data is consistent with other studies showing deficits in working memory and with MRI studies showing decreased thickness in regions of the hippocampus, a key brain region for memory formation, in adults with a history of heavy cannabis use[4,5]. On average, college students who report cannabis use have lower grade point averages (GPAs) than those who do not, though GPAs improved if use was halted[6]. In contrast to above, a randomized controlled-trial of cannabis has been done in adults and demonstrated decreased verbal memory and working memory after smoking cannabis[7].
I think it is important to note that brain development is a process that continues into the 20s, maybe even the early 30s, with the frontal lobes of the brain being the last to fully develop. This is the area of the brain associated with executive function and decision making, thus why you must be 18 years of age to sign a contract. Therefore, it makes sense that long-term use of a potentially toxic substance like cannabis – especially when started early in life – may have long-term consequences. Granted, if you have a genius IQ in the 170s, a loss of 8 points may still leave you a genius, but if you have an average IQ of 100, 8 points may have significant consequences.
The article is accurate in describing the scientific study. The headline is also linguistically accurate, as it says “could”, rather than “does.” My concern is that the article provides inappropriate and inadequate context for the study it describes. It acknowledges that marijuana may not be the “sole reason” for the IQ decrease, mentioning socioeconomic status as another factor. In fact, the true uncertainty is that marijuana use may not be a factor at all, with the entire observed effect due to socioeconomic status or other unknown or unmeasured factors. This is the important limitation of all associational studies, which I believe should be mentioned in all accounts of such studies (but is not mentioned in this article), viz., association can only suggest causation, but never prove it.
The article does not mention that not all published, well-designed longitudinal studies are consistent in showing an association between cannabis use and impaired cognition[3,8,9]. However, I do agree with the current consensus, implied in this article, that adolescent cannabis use probably does modestly impair cognitive function.
In addition, I disagree with the article’s definitive statement that an 8-point IQ decrease is functionally significant. I am not an expert on IQ, but my impression of the literature is that there is not a close association between IQ and so-called executive function (e.g., cognitive judgement, decision-making) as assessed by psychological tests, especially at normal to high IQ levels[10]. However, information on any association between IQ and life function is best left to an IQ specialist.
The National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine (NAS) published a review in 2017 on the health effects of cannabis[11]. In their evaluation of the cognitive effects of cannabis in adolescents, they examined memory, learning and attention, explaining that:
“In terms of the relevance of these aspects of cognition, the domains of learning, memory, and attention are central, as they undergird an individual’s success—or failure—across such areas as academic, employment, and social/relationship functioning. This subsequently renders these three domains of cognition strong proxies for examining interference in functioning.“
In the NAS’ evaluation of relevant literature reviews published between 2000 and 2016, they found only limited evidence showing an association between cannabis use and sustained negative consequences for these three domains (“sustained” is defined as continuing even “after a period of abstinence from cannabis”).
A few more studies published after 2016 also examined this topic and came to similar conclusions. A study by Schuster et al. showed that early onset of marijuana use (16 years old or younger) was associated with significantly poorer verbal memory functioning and impeded learning in young adults between 18 – 25 years old[12]. A follow-up study by Levar et al. published in 2018 showed similar findings and also showed changes in brain structure that may underpin poorer verbal memory in early-onset cannabis users[13].
A study by Auer et al. found evidence that cumulative years of cannabis use was associated with worse verbal memory, but not in the other measures of cognitive function (processing speed and lower executive function)[14]. However, it is not clear if this observation also held true for individuals who were abstaining from cannabis use at the time of the study.
NOTES & REFERENCES
- 1 – Meier et al. (2012). Persistent cannabis users show neuropsychological decline from childhood to midlife. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
- 2 – Moffitt et al. (2013). Reply to Rogeberg and Daly: No evidence that socioeconomic status or personality differences confound the association between cannabis use and IQ decline. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
- 3 – Meier et al. (2018). Associations between Adolescent Cannabis Use and Neuropsychological Decline: A Longitudinal Co-Twin Control Study. Addiction.
- 4 – Chye et al. (2017). Cannabis-related hippocampal volumetric abnormalities specific to subregions in dependent users. Psychopharmacology.
- 5 – Owens et al. (2018). Urinary tetrahydrocannabinol is associated with poorer working memory performance and alterations in associated brain activity. Neuropsychopharmacology.
- 6 – Martinez et al. (2015). How Robustly Does Cannabis Use Associate to College Grades? Findings From Two Cohorts. Journal of Drug Education.
- 7 – Hindocha et al. (2017). Acute memory and psychotomimetic effects of cannabis and tobacco both ‘joint’ and individually: a placebo-controlled trial. Psychological Medicine.
- 8 – Gonzalez et al. (2017). Does Cannabis Use Cause Declines in Neuropsychological Functioning? A Review of Longitudinal Studies. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society.
- 9 – Morin et al. (2018). A Population-Based Analysis of the Relationship Between Substance Use and Adolescent Cognitive Development. American Journal of Psychiatry.
- 10 – Arffa et al. (2007). The relationship of intelligence to executive function and non-executive function measures in a sample of average, above average, and gifted youth. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology.
- 11 – National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine. (2017). The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.17226/24625
- 12 – Schuster et al. (2017). Early Onset Marijuana Use Is Associated with Learning Inefficiencies. Neuropsychology.
- 13 – Levar et al. (2018). Verbal Memory Performance and Reduced Cortical Thickness of Brain Regions Along the Uncinate Fasciculus in Young Adult Cannabis Users. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research.
- 14 – Auer et al. (2016). Association between Lifetime Marijuana Use and Cognitive Function in Middle Age: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. JAMA Internal Medicine.