Is President Trump right that polar ice caps are setting records for growth, instead of melting?


SOURCE: Donald Trump, ITV, 28 Jan. 2018
Imprecise: The term “ice caps” makes it unclear what President Trump intends to refer to. An ice cap is one technical category of glacial ice on land, not a catch-all term for polar sea ice and glaciers..

SCIENTISTS’ REVIEW
In a January interview with ITV, President Trump claimed that the ice caps are not melting but are setting records: “The ice caps were going to melt. They were going to be gone by now, but now they’re setting records, okay? They’re at a record level.”
Polar scientists from the Climate Feedback network who reacted to this claim all explained that it was inaccurate, and in direct contradiction with available evidence.

Physical Oceanographer, British Antarctic Survey
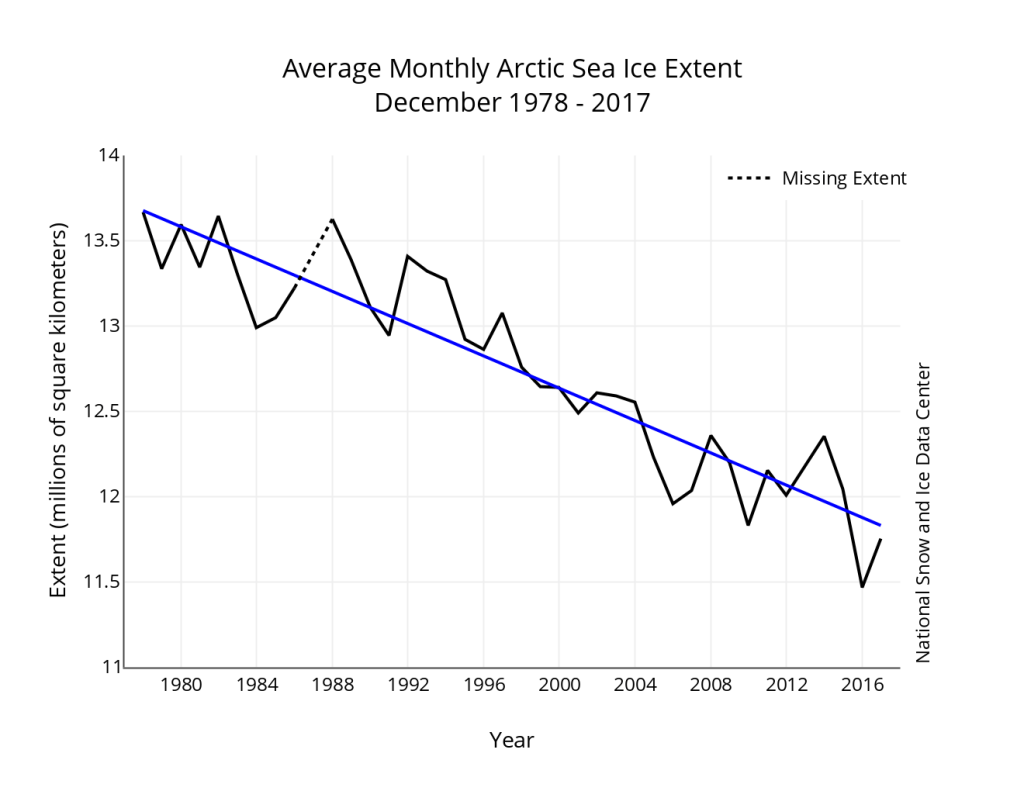
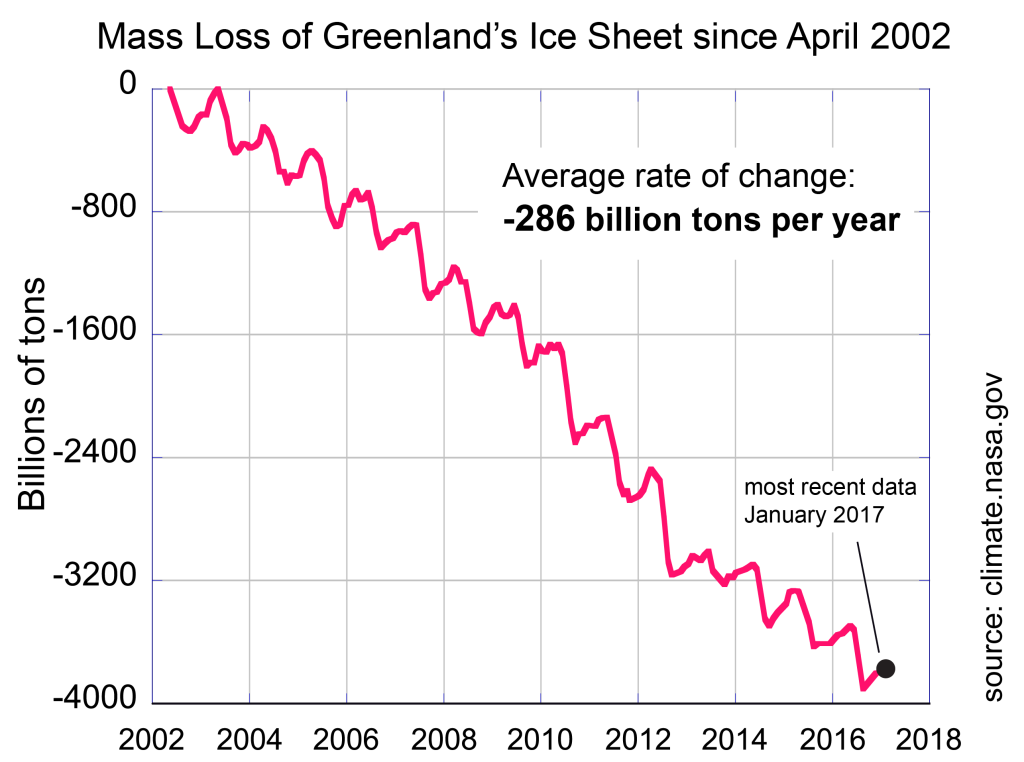
This claim is misleading in the extreme—the ice caps are indeed setting records, but not in the way President Trump is implying. The USA’s own National Snow and Ice Data Center shows that December 2017 was the second lowest December extent on record for Arctic sea ice extent (see below), and the Greenland ice sheet continues to set record lows (see below). Antarctica is also losing land ice, and at an accelerating rate*.
- Shepherd et al (2012) A Reconciled Estimate of Ice-Sheet Mass Balance, Science

Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Université catholique de Louvain
President Trump uses the wording “ice caps”. This wording itself is not precise, as defined in the American Meteorological Society glossary—it is not clear whether President Trump is referring to ice sheets, sea ice, or glaciers. Given the start of the next sentence, I assume he is referring to sea ice.
On the statement that “They [ice caps, meaning sea ice as I understand him] were going to be gone by now”: To my knowledge, only two scientists (P. Wadhams and M. Maslowski) predicted that an ice-free Arctic would have already occured in summer by now (but this has obviously not been the case). [Previous Climate Feedback evaluations have rated the credibility of Wadhams’ claim.] Both statements were made by extrapolating the observed record and model output, respectively. This method ignores (1) the existence of powerful negative feedbacks that make the ice grow faster when it is thinner1, and (2) the existence of strong interannual variability that interplays with the long-term decline2. A thorough assessment of the scientific literature carried out in the latest IPCC report reveals that the Arctic is likely to become ice-free in summer by mid-century.
On the statement that “They are setting records”: Yes, they are, but they are setting record lows. Given the first part of his sentence, I assume that President Trump meant “record highs”, so he is wrong. Global sea ice extent (Arctic + Antarctic) has been lowest in 2016 and 2017 compared to the historical record. Arctic sea ice extent has been declining for decades. Antarctic sea ice extent displayed moderate increases from 1979 to 2014 but has considerably decreased since then.
- 1- Bitz and Roe (2004) A Mechanism for the High Rate of Sea Ice Thinning in the Arctic Ocean, Journal of Climate
- 2- Swart et al (2015) Influence of internal variability on Arctic sea-ice trends, Naure Climate Change

Research Scientist, University of Colorado, Boulder
No part of this statement is true. Regarding the specific claim about ice sheets, this is false. The large ice sheets or ice caps do not have more ice now than they would have without human-caused climate change. The opposite is true—the world’s ice sheets and glaciers have less ice because of human-caused climate change. The Greenland and Antarctic Ice Sheets and glaciers and other large ice areas (e.g. in Alaska, Canada, Patagonia, Himalayas, etc.) are collectively losing hundreds of gigatons of ice per year and directly raising ocean levels, among other impacts.
There is a small mountain of research on ice sheet behavior, which all clearly points to ice loss due to human-caused change. For evidence that human-caused warming is the main factor in glacier ice loss, Roe et al is a good reference*.
The issue of “climate change” versus “global warming” is only a topic of word choice and in no way reflects a changes in the patterns of ice behavior that scientists are observing worldwide. Nature does not care about word choice.
- Roe et al (2017) Centennial glacier retreat as categorical evidence of regional climate change, Nature Geoscience

Postdoctoral research fellow, University of Reading
President Trumps comments that “The ice caps were going to melt. They were going to be gone by now” may be the result of predictions made a few years ago by an overly enthusiastic Arctic scientist who I choose not to name here. At the time the climate science community rejected such extreme predictions, however the headlines stuck and return here to the detriment of the community and the planet.
It is not clear whether presidents Trump’s comments on record setting are intentionally ambiguous, but one can assume he feels they are at record high levels based on the context. According to NASA data, Land Ice in Antarctica has lost 2000 Gt in the last 15 years, while the Greenland ice sheet has lost almost 4000 Gt over that period. As far as sea ice is concerned both the Arctic and Antarctic are currently (Jan 2018) running at a negative extent anomaly, which combined totals to -2,439,000 km2 using NSIDC data, trends in sea ice thickness and volume are even greater.
President Trump also mentions there’s cooling and there’s heating. This is somewhat true and is the natural variability of the climate. The trouble is that human influence means that on average we now see a lot more heating than cooling, a trend we don’t expect to change anytime soon.
Viral NASA video shows sea ice decline
In contrast, an article published by Fox 2 St. Louis in February 2018—based on an article syndicated from CNN—noted that 2017 ranked as one of the warmest year on record, and annually averaged sea ice extent in the Arctic was at its second lowest extent.
This article has been shared more than 1.2 million times on social media as of January 2019, making it the most popular climate story of 2018!
The article featured a video made by NASA that shows the reduction in coverage of older, thicker sea ice in the Arctic over the past decades.
Scientists who reviewed the article and video indicated that it was of high scientific credibility.

Professor, University of Reading and UK National Centre for Earth Observation
The NASA movie [above] shows the power of being able to visualise what has been happening to the environment over many years, in this case for Arctic sea ice. The evidence of change is plain to see. The facts-driven description in the article that accompanies the movie addresses developments in other parts of Earth’s climate system straightforwardly and informatively.

Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Université catholique de Louvain
The article is factually correct. The reality that Arctic sea ice is getting younger [rather than surviving for several years and growing thicker] is not so well known from the public, so such an article is welcome.The article’s title and the front video are about sea ice, but most of the rest of the text is about global temperatures. There has been clear evidence that the two (rising temperatures and declining sea ice) are linked on long time scales (say, >15 yr), but interannual fluctuations of the latter are more difficult to formally relate to the former.