Insight into the scientific credibility of The Guardian climate coverage
Over the past two months, Climate Feedback has asked its network of scientists to review 5 widely read articles published…
Latest in

Over the past two months, Climate Feedback has asked its network of scientists to review 5 widely read articles published…
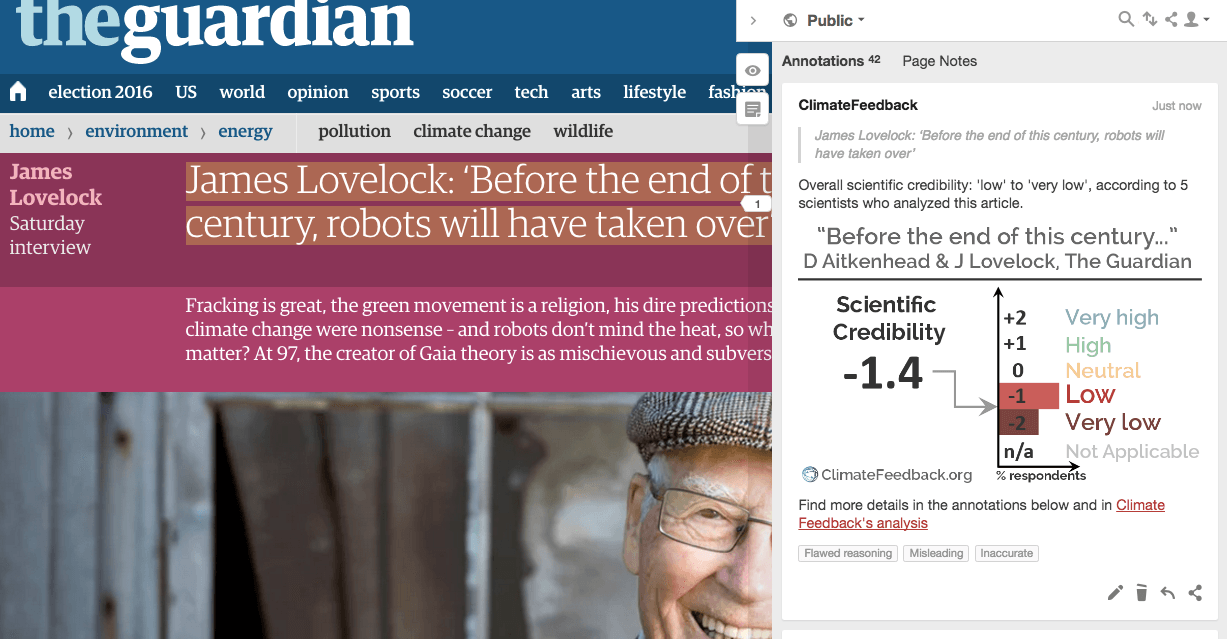
“Extraordinary claims demand extraordinary evidence, and Lovelock has not even come up to the standards of providing what the scientific community would consider to be ordinary evidence. The journalist did not balance Lovelock’s statements with a set of clear statements saying that the vast majority of informed climate scientists (as, for example, represented by the IPCC reports) have reached consensus on conclusions that are diametrically opposed to what Lovelock is saying, and that the IPCC scientists have backed up their statements with a wealth of empirical data, whereas Lovelock is largely opining without providing any substantive evidence to support his rather extraordinary claims.”
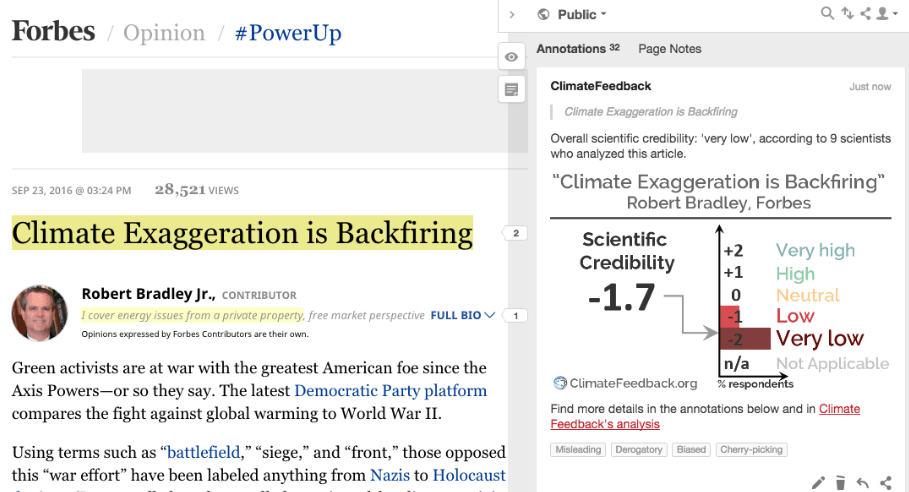
“This picking of quotes that are convenient for Robert Bradley Jr.’s narrative while ignoring what most climate scientists say is one of the most used rhetorical tools of this piece. The other is the use of offensive emotional language to reduce the critical thinking of his readers. People should know that Forbes is nowadays just a blogging platform.”
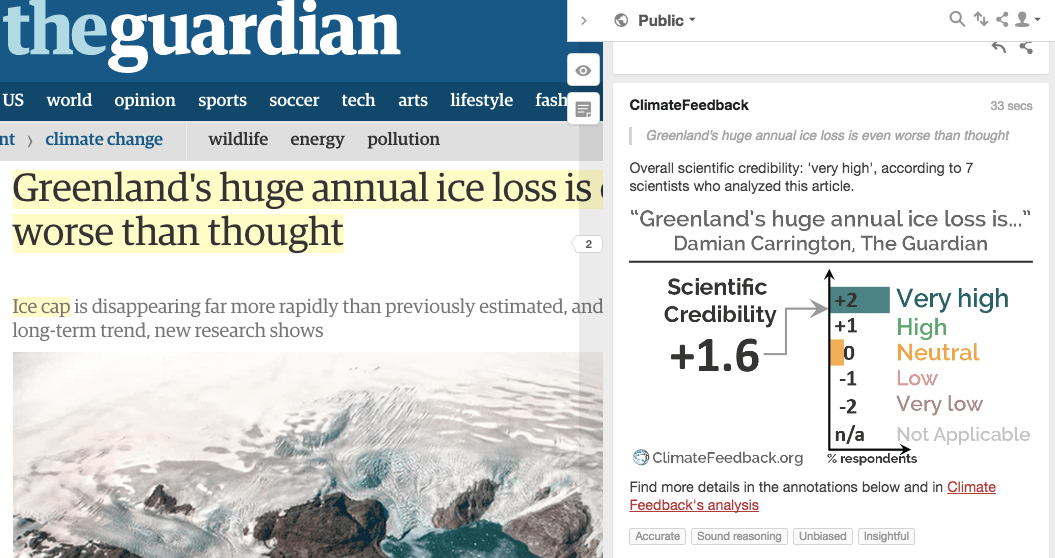
“I find the headline accurate and supported by the article. The article explains the novelty and impact of the research accurately for the general readership and in particular the context provided from the scientists works really well in this regard.”
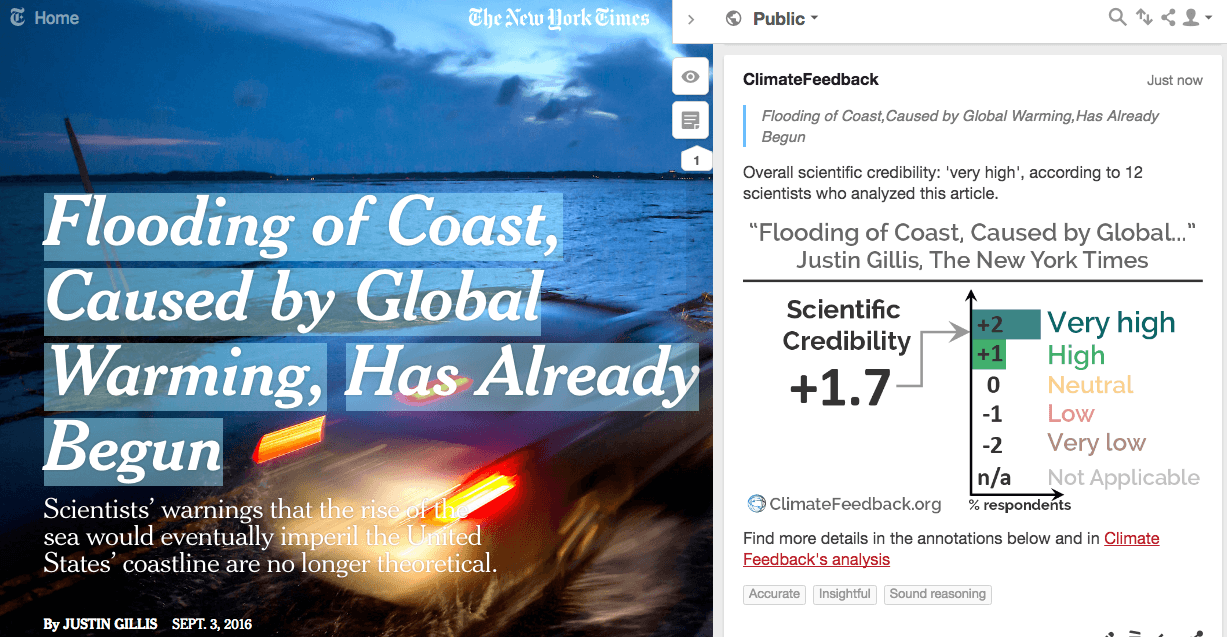
“The theory of sea-level rise and flood problems is pretty well understood — this makes the point that this theory is also happening now and can only be expected to get worse — sea levels have been rising on the US east coast for the last 150 years or more and even if current trends simply continue, impacts will continue to grow. As the article states, we actually expect a significant acceleration of sea-level rise in the coming decades meaning the impacts will grow more rapidly.”

Claim:
Sea level rise could reach six or seven feet by the year 2100.
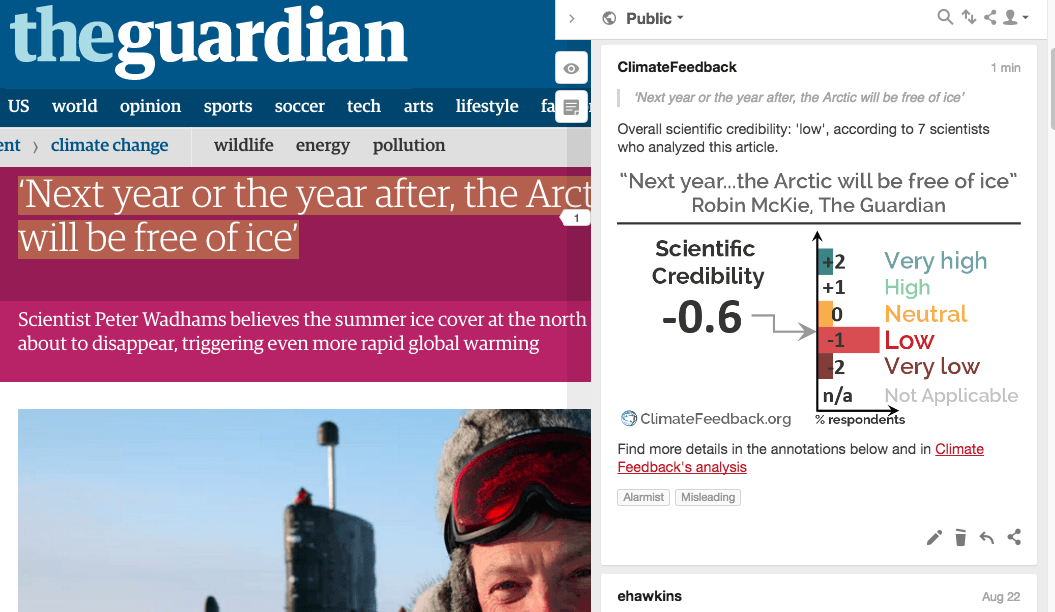
“before propagating a marginal view, one should ensure having a very strong argumentation; in this interview no argumentation is put forward to support Peter Wadhams’ central claim. Wadhams’ alarmism is potentially harmful, because when such spectacular predictions are not realized some people may perceive the whole scientific community or science itself as untrustworthy.”
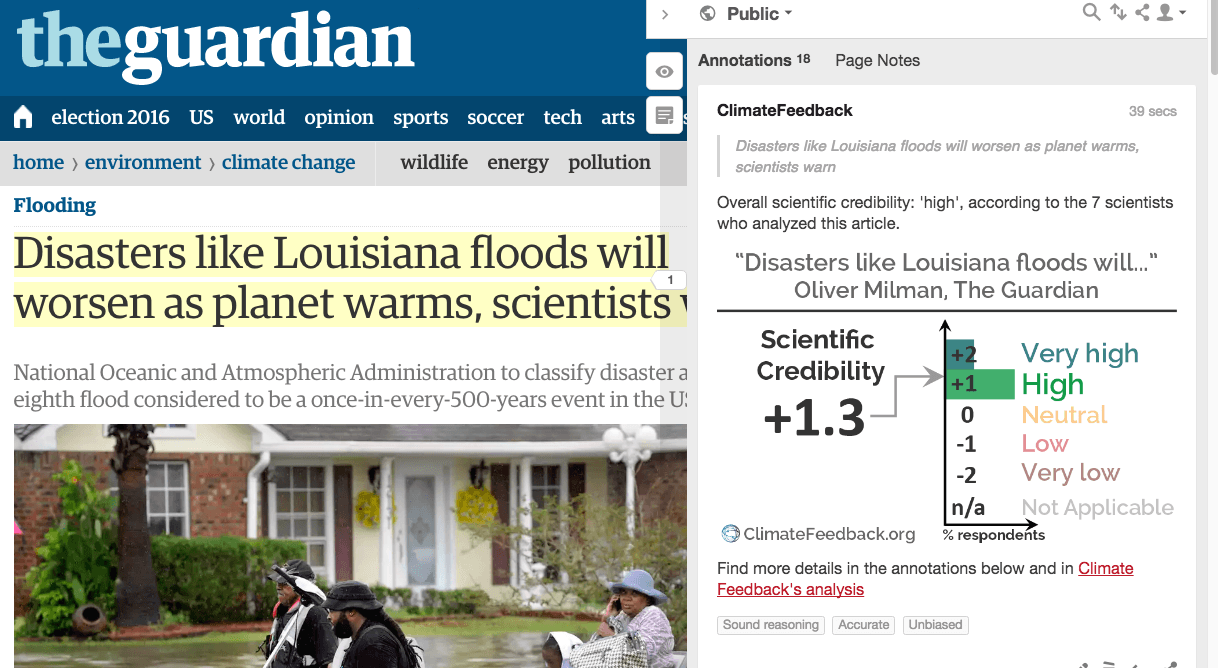
“this article does a good job reporting on the recent floods in Lousiana and, more generally, the climate-change-induced changes in the water cycle that underlie scientists’ concerns about future increase in floods. However, “heavy rainfall” is not strictly synonymous to “flooding”…”
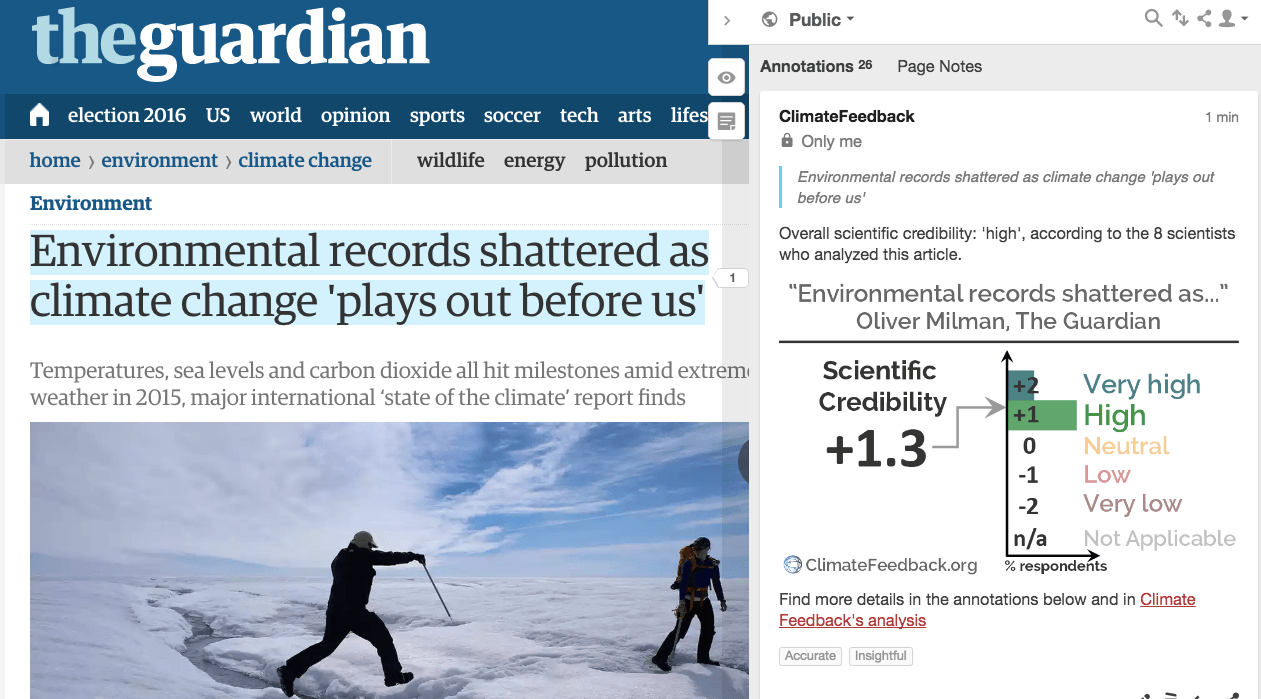
The article summarizes the main findings of the “2015 state of the climate” report published by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Overall it accurately reports the main findings that many global indicators of the Earth’s climate, notably the global surface temperature, have set new records in 2015 under the joint influence of ongoing human-induced climate change and a strong El Niño event.
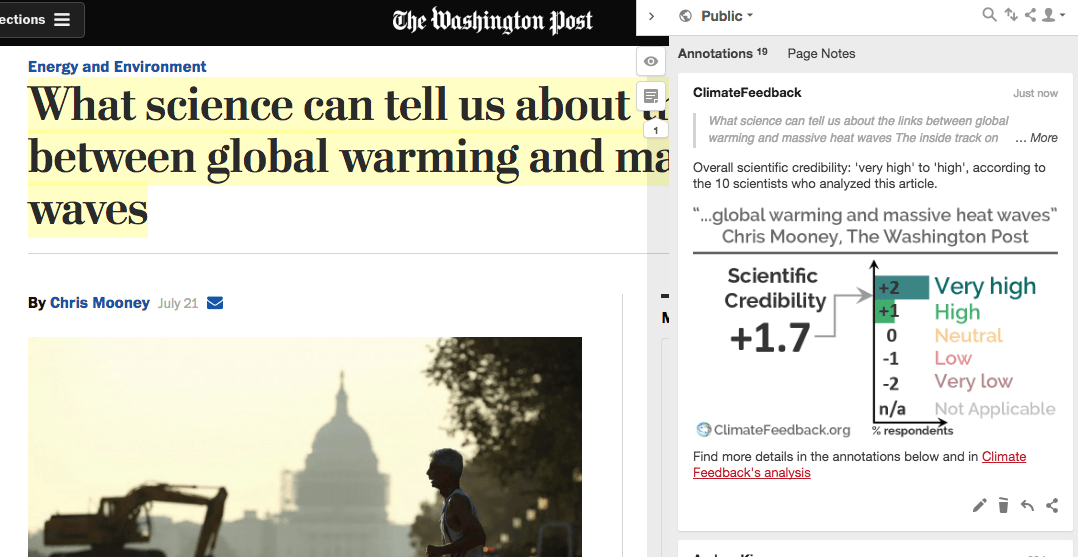
“This is a well-written article that provides a good overall discussion around the connection between climate change and the ongoing US heat wave. In the absence of a specific event attribution study the role of climate change in this event can’t be quantified, but Chris Mooney provides an insightful overview of the role of climate change in heat events generally.”